is dna a carbohydrate Digestion dna carbohydrates role module lesson section physiological nad deoxyribose
Carbohydrates are a vital component of our body’s biochemistry. They are one of the four main macronutrients that our bodies require to sustain life, and they play critical roles in a wide variety of physiological processes. Today, let’s dive deeper into carbohydrates biochemistry and understand their numerous roles in our bodies. Carbohydrates are molecules containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a ratio of 1:2:1. Their primary function is to provide energy to our cells, tissues, and organs. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, the primary energy source for our bodies. Our brain and red blood cells exclusively rely on glucose for fuel. There are three main types of carbohydrates - monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates, consisting of a single sugar molecule. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Disaccharides are composed of two sugar molecules, such as sucrose, lactose, and maltose. Polysaccharides are compounds that contain many sugar molecules chemically linked together, such as starch and glycogen. Carbohydrates also play an essential role in forming our genetic material, DNA, and RNA. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) contains a sugar molecule called deoxyribose, while ribonucleic acid (RNA) contains a sugar molecule called ribose. These sugar molecules provide the backbone of the DNA and RNA structures. The physiological roles of carbohydrates extend beyond energy provision and genetic material formation. Cellulose, a polysaccharide, is the primary component of plants’ cell walls. Human enzymes cannot break down cellulose, but it serves as an important source of dietary fiber, which is crucial to maintaining healthy bowel movements and preventing bowel diseases. Another vital role of carbohydrates is to provide structural support and protection. Chitin, a type of polysaccharide, forms the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans. Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), another type of carbohydrate, are essential components of connective tissues such as cartilage and tendons. GAGs attract and bind water, giving the tissues their characteristic elasticity and shock-absorbing properties. In conclusion, carbohydrates play numerous important roles in our bodies’ biochemistry, including energy provision, genetic material formation, structural support and protection, and more. Understanding the significance of carbohydrates to our health can help us ensure that our diets contain an appropriate amount and variety of carbohydrates.
If you are looking for Carbohydrates Biochemistry Short Notes | EasyBiologyClass you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Pictures about Carbohydrates Biochemistry Short Notes | EasyBiologyClass like Carbohydrates Biochemistry Short Notes | EasyBiologyClass, Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids and Nucleic Acids and also Blog Carbohydrates. Here you go:
Carbohydrates Biochemistry Short Notes | EasyBiologyClass
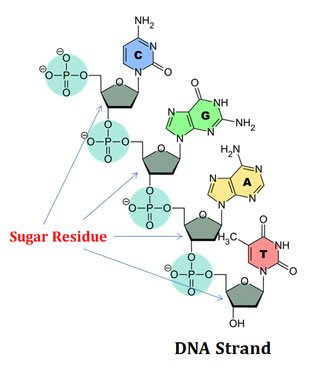 www.easybiologyclass.comcarbohydrates dna biochemistry notes sugar carbohydrate classification biology easybiologyclass genetic material introduction biological choose board simple properties
www.easybiologyclass.comcarbohydrates dna biochemistry notes sugar carbohydrate classification biology easybiologyclass genetic material introduction biological choose board simple properties
Blog Carbohydrates
 mateo2426.weebly.comnucleic carbohydrates
mateo2426.weebly.comnucleic carbohydrates
Cover Picture: Application Of Biocatalysis To On‐DNA Carbohydrate
 onlinelibrary.wiley.comSection 2: Module 3: Lesson 1: Carbohydrates - Physiological Role
onlinelibrary.wiley.comSection 2: Module 3: Lesson 1: Carbohydrates - Physiological Role
 triagemethod.comdigestion dna carbohydrates role module lesson section physiological nad deoxyribose
triagemethod.comdigestion dna carbohydrates role module lesson section physiological nad deoxyribose
Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids And Nucleic Acids
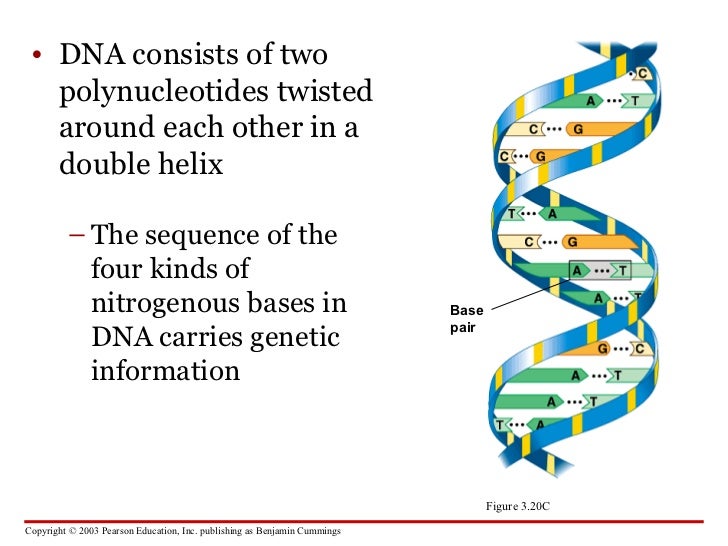 www.slideshare.netcarbohydrates lipids dna nucleic acids
www.slideshare.netcarbohydrates lipids dna nucleic acids
Carbohydrates biochemistry short notes. Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids. Cover picture: application of biocatalysis to on‐dna carbohydrate